MODBUS
Introduction
MODBUS is a widely adopted communication protocol used in industrial automation and control systems. Developed in 1979 by Modicon (now Schneider Electric), MODBUS has become a standard method for transmitting information over serial lines between electronic devices. Originally designed to work with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), MODBUS is now used in a variety of applications and is compatible with a broad range of devices.

What is MODBUS?
MODBUS is a protocol that facilitates communication between multiple devices connected to the same network. It operates on a master-slave or client-server architecture where a master device (such as a computer or a PLC) initiates queries to slave devices (such as sensors, actuators, or other PLCs), which then respond with the requested data. This simplicity and reliability have contributed to MODBUS’s longevity and widespread use.
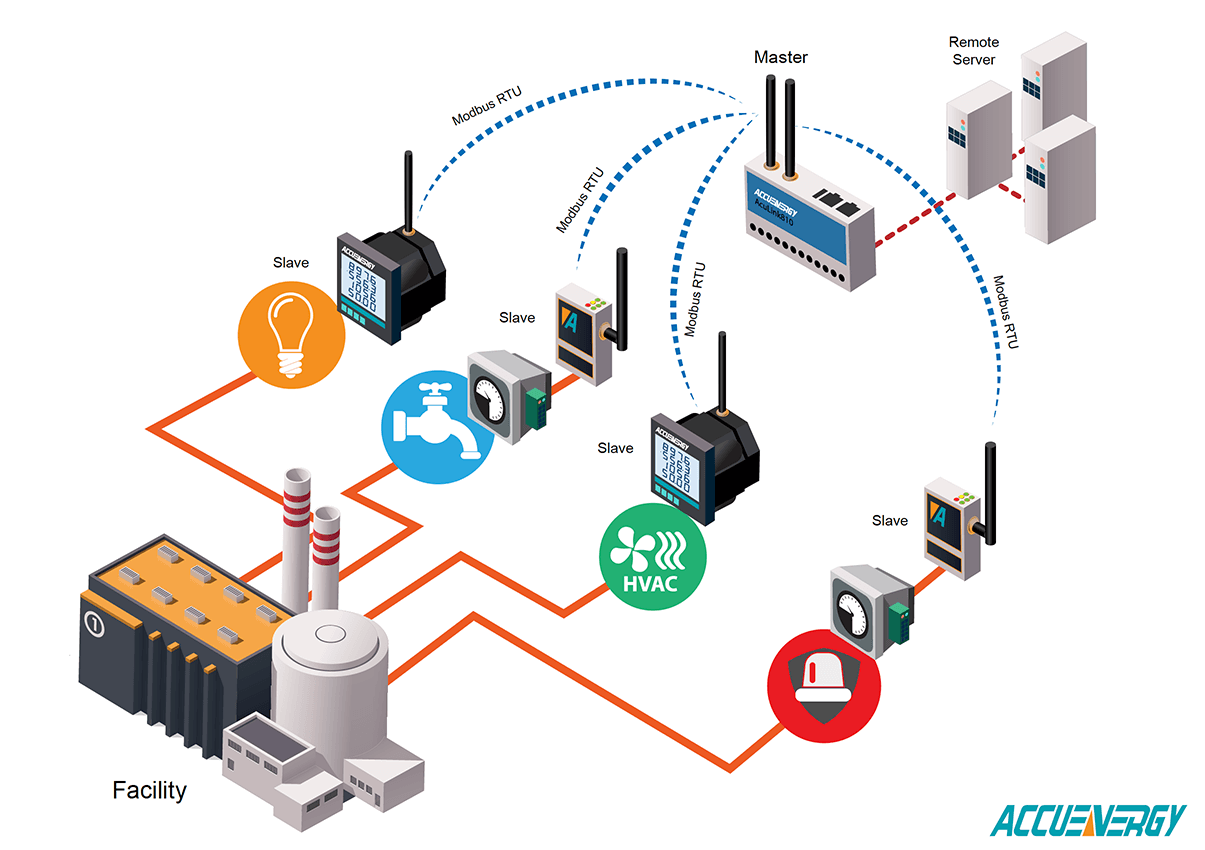
Key Features of MODBUS
Simplicity and Flexibility: MODBUS is easy to implement and understand, making it a popular choice for various industrial applications. Its open and simple structure allows for easy integration and customization.
Compatibility: MODBUS is supported by a wide range of devices and manufacturers, ensuring interoperability across different equipment and systems.
Scalability: MODBUS can be used in both small-scale systems with a few devices and large-scale systems with hundreds of devices. This scalability makes it a versatile choice for different project sizes.

Real-time Communication: MODBUS enables real-time data exchange, making it suitable for applications where timely updates are critical, such as in process control and monitoring systems.
Efficient Data Handling: The protocol is designed to handle data efficiently, minimizing the overhead in communication. It supports the transmission of data in discrete bits or in groups of 16-bit words, optimizing the use of network bandwidth.
